KIWI BIRD, FLIGHTLESS BIRDS, NEW ZEALAND, EGG, SIZE, FACTS, IMAGES, VIDEOS, DRAWING, EXTINCT
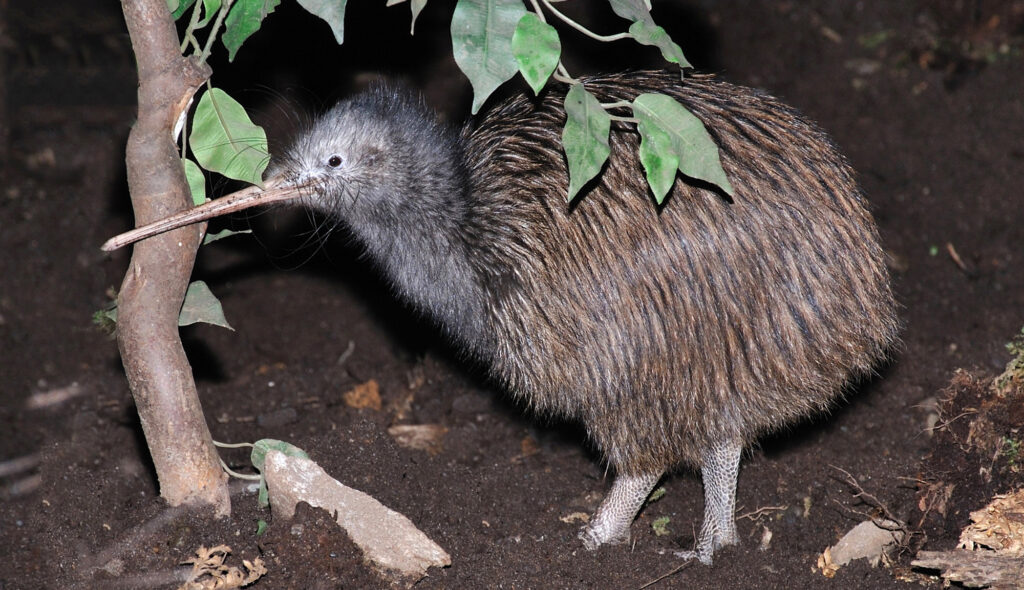
To begin with, the kiwi bird (Apteryx mantelli) is a species native to New Zealand and is considered a national symbol of the country. Despite its distinctive appearance, the kiwis bird is also known for its unique biology and behavior.
KIWI BIRD CHARACTERISTICS
One of the most recognizable features of the kiwi bird is its long beak, which is used to probe for food in the ground. The kiwi is also flightless, with small, vestigial wings that are covered in feathers. The species is also nocturnal, which makes it difficult to observe in the wild.
UNIQUE BIOLOGY
Another interesting aspect of the kiwis bird is its biology. Unlike most birds, the kiwi has a highly developed sense of smell, which it uses to locate food. The species is also unique in that it has a backward-facing reproductive tract, which makes it the only bird species to lay eggs that are large in proportion to its own body size.
HOW LONG DO KIWIS BIRD LIVE?
Kiwis birds can live for a relatively long time in the wild, with some individuals reaching up to 20 years of age. The average lifespan of a kiwi bird in the wild is about 10-15 years, but this can vary depending on a variety of factors, such as predation, disease, and habitat degradation.
In captive breeding programs, kiwi birds can live even longer, sometimes reaching up to 25 years of age. This is due to the controlled conditions and access to veterinary care that these birds receive in captivity.
Overall, the lifespan of a kiwis bird is influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, diet, predation, disease, and habitat quality. By protecting their habitats and managing threats like predation and disease, we can help to ensure the long-term survival of kiwi birds and extend their lifespan in the wild.
WHAT’S THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN MALES AND FEMALES KIWIS?
To pursue, the main difference between male and female kiwis birds is that the male kiwi bird is generally larger and has a longer bill than the female. This is a characteristic of many bird species and is thought to be related to the different roles that male and female birds play in the breeding process.
In the case of the kiwi bird, the male is responsible for incubating the eggs, so he needs to be larger and have a longer bill to regulate the temperature of the eggs more effectively. The female, on the other hand, is responsible for laying the eggs and does not need to be as large or have a long bill for this task.
It’s important to note that there can be variation in size and bill length within populations of kiwi birds, and not all males are larger or have longer bills than all females. However, on average, the male kiwi bird is generally larger and has a longer bill than the female.
WHERE CAN WE FIND THE KIWI BIRD?
Kiwi birds are found only in New Zealand and are indigenous to the country. They are not found anywhere else in the world.
Within New Zealand, kiwi birds are primarily found in the native forest habitats of the North Island and the northwest of the South Island. They are also found in some offshore islands and protected areas, where they have been introduced to reduce the impact of predators like stoats and feral cats.
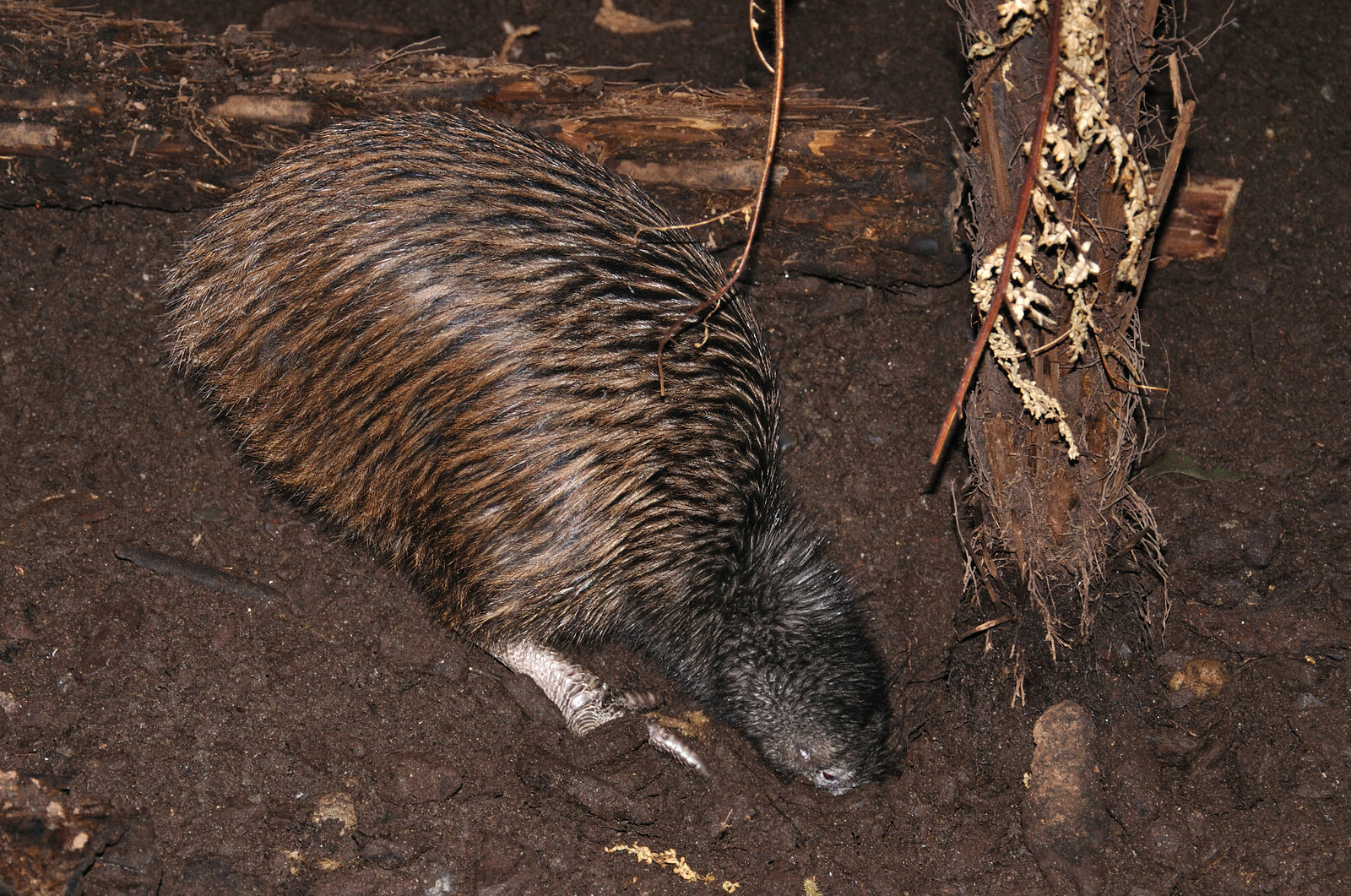

North island brown kiwi, apteryx australis, buries its beak in the ground, searching for food, new zealand
WHAT IS THE SIZE OF KIWI BIRDS?
The size of a kiwi bird varies depending on the species, but in general, kiwi birds are relatively small, flightless birds. The smallest species of kiwi, the little spotted kiwi, can weigh as little as 1 kilogram (2.2 pounds), while the largest species, the great spotted kiwi, can weigh up to 4 kilograms (8.8 pounds).
In terms of length, kiwi birds can range from about 40 centimeters (16 inches) to more than 50 centimeters (20 inches), with their long, thin bills accounting for much of their overall length. They are also characterized by their small wings, which are too small to allow them to fly, and their long, powerful legs, which are adapted for running and burrowing.
Overall, the size of a kiwi bird is relatively small compared to many other birds, but they make up for it with their unique and fascinating adaptations, such as their long bill, powerful legs, and keen senses, which help them to thrive in their native habitats in New Zealand.
HOW ARE KIWI BIRD EGGS?
Kiwi birds have eggs that are relatively large and distinctive compared to the eggs of most other birds. Kiwi bird egg are about 10-20% of the female’s body weight, which is significantly larger than the eggs of most birds, which are usually only a few percent of the female’s body weight.
For the shape, kiwis eggs are oval and have smooth, glossy surfaces. They are usually brown in color, with a mottled pattern that helps them to blend in with their forested habitats.
The large size of kiwi bird egg is an adaptation to their flightless and nocturnal lifestyle. The large eggs provide a more nutritious and calorie-rich food source for the developing embryo, which allows it to grow and develop more quickly, as well as providing a larger yolk sac, which is a critical source of nutrients for the hatchling.
KIWIS ARE FACING THREATS
The kiwi bird faces many threats in the wild, including habitat loss and predation by introduced mammals such as stoats, ferrets, and weasels. Conservation efforts have been undertaken to protect the species and its habitat, including predator control programs, breeding and release programs, and public education campaigns.
SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH ON KIWI BIRDS
In addition to conservation efforts, research on the kiwi bird is ongoing and is providing valuable insights into its biology and behavior. For example, studies have shown that the kiwi is a highly social species, with complex social structures and interactions. This information can be used to inform future conservation efforts and ensure that the kiwi bird remains part of New Zealand’s natural heritage for generations to come.
PUBLIC EDUCATION
Another important aspect of kiwi conservation is public education. Many people may not be aware of the threats facing the kiwi bird and the importance of protecting it. By raising awareness and educating the public about the species, people can become more invested in its conservation and take action to protect it.
ECOTOURISM
In recent years, ecotourism has also emerged as an important tool for kiwi conservation. By offering visitors the opportunity to observe kiwi birds in their natural habitat, ecotourism can help generate support and funding for conservation efforts. This can include guided tours, wildlife watching, and research projects that allow visitors to directly contribute to the conservation of the species.

CULTURAL SIGNIFICANCE
Indeed, it is important to recognize the cultural significance of the kiwi bird. For the indigenous Māori people of New Zealand, the kiwi bird is a powerful symbol of the country’s natural heritage and cultural identity. By protecting the kiwi bird, we not only preserve an important species, but also the cultural heritage and traditions of the Māori people.
HOW TO SUPPORT KIWI BIRDS CONSERVATION?
One way to further support kiwi conservation is through responsible and sustainable tourism. When visiting areas where kiwi birds live, it is important to follow established guidelines to minimize the impact on their habitat and reduce the risk of spreading diseases or other harmful organisms. Visitors can also support conservation organizations by making donations or participating in conservation activities, such as planting native vegetation or controlling invasive species.
HABITAT PROTECTION
In New Zealand, many areas of kiwi habitat have been set aside as protected conservation lands, including national parks, wildlife refuges, and private reserves. Besides, conservation organizations are working to establish predator-free zones where kiwi birds can thrive without the threat of predation.
ECONOMIC BENEFITS OF KIWI BIRD PROTECTION
Nonetheless, it is also important to consider the economic benefits of kiwis birds conservation. The kiwi bird is an important cultural icon and a valuable tourism asset, bringing significant economic benefits to local communities. Ecotourism can provide a source of income for local people while also promoting conservation efforts.
Additionaly, kiwi conservation can also contribute to the development of new technologies and techniques that can be applied to other conservation efforts. For example, the development of predator control methods for kiwi conservation can also be applied to the conservation of other endangered species.
SOCIAL BENEFITS
Furthermore, kiwi conservation can also have positive social and cultural benefits. By educating local communities and visitors about the importance of the kiwi bird and its habitat, we can promote a greater understanding of and appreciation for biodiversity and the natural world. This can contribute to a sense of pride and connection to the environment and increase support for conservation efforts.
In conclusion, the kiwi bird is a fascinating and unique species that deserves continued protection and preservation. Through a combination of conservation efforts, community engagement, international cooperation, and a recognition of the economic, technological, social, and cultural benefits of kiwi conservation, we can ensure the long-term survival of this fascinating species and protect a part of New Zealand’s natural and cultural heritage.
WANT TO LEARN MORE? TAKE A LOOK AT THESE ARTICLES:
- The Scarlet Macaw
- The Scarlet Ibis
- Lovebirds
- The Female Cardinal
- The Great Egret
- The Great Blue Heron
- The American Robin
- The Northern Cardinal
- The Dark-Eyed Junco
- The Blue Jay
- The Gray Catbird
- The Tufted Titmouse
- The Red-winged Blackbird
- The Black-capped Chickadee
- The Evening Grosbeak
- The Common Starling
- The Kiwi Bird
- Wild Birds Unlimited

